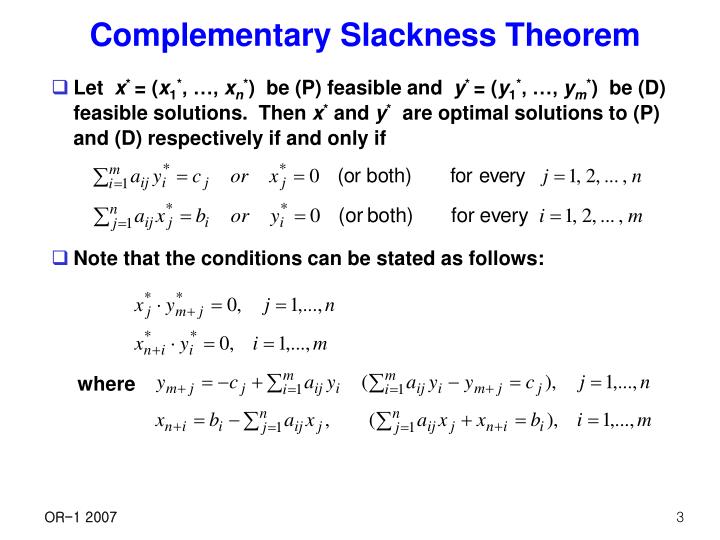
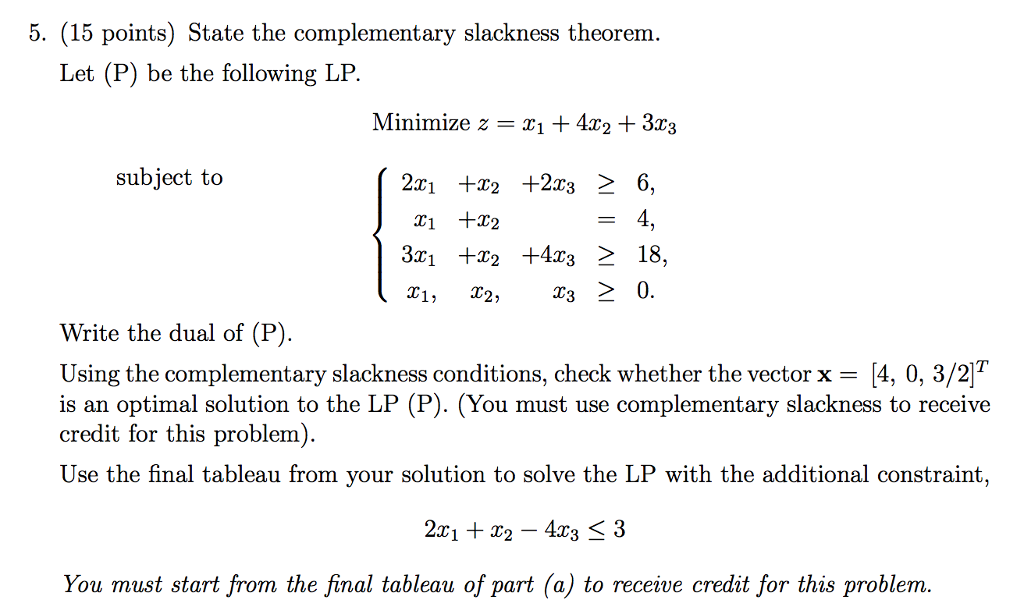
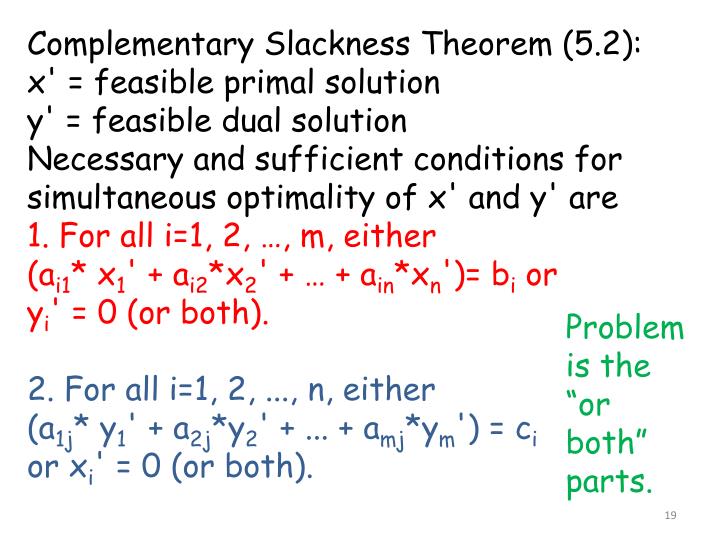
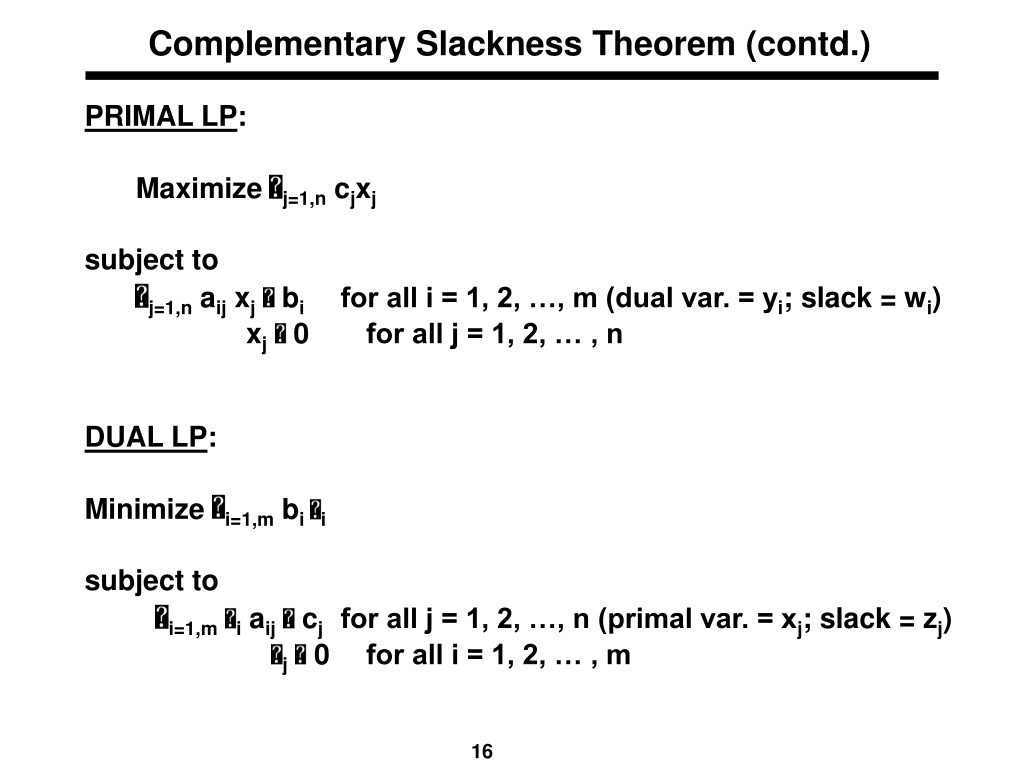
Complementary Slackness Theorem
Complementary Slackness Theorem - Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions.
Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions. Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming.
The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions.
PPT Relationship between (P) & (D) PowerPoint Presentation ID3895569
Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions. Let p and.
Complementary slackness and farkas lemmaa
Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Let p and d denote the.
V412. Linear Programming. The Complementary Slackness Theorem. part 2
Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. One thing we can.
5. (15 points) State the complementary slackness
The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between.
1 Complementary Slackness YouTube
Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify.
complementary slackness theorem with examples YouTube
Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x.
V411. Linear Programming. The Complementary Slackness Theorem. YouTube
Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to.
PPT Summary of complementary slackness 1 . If x i ≠ 0, i = 1, 2
One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. The complementary slackness1 theorems state. Let x be a primal.
PPT DUALITY THEORY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9471038
Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. Let p and d denote the primal and dual.
The Complementary Slackness Theorem (explained with an example dual LP
Let x be a primal feasible solution and let u be a dual feasible solution such that complementary slackness holds between x and. Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions..
The Complementary Slackness1 Theorems State.
Say someone tells us that \(x_1^* =. Theorem (complementary slackness) let x be a feasible solution to the primal and y be a feasible solution to the dual where primal max c x ax b. One thing we can use complementary slackness for is to verify claims about optimal solutions. Learn how to use complementary slackness conditions to check the optimality of primal and dual solutions in linear programming.
Let X Be A Primal Feasible Solution And Let U Be A Dual Feasible Solution Such That Complementary Slackness Holds Between X And.
Let p and d denote the primal and dual linear program (in standard form) respectively.