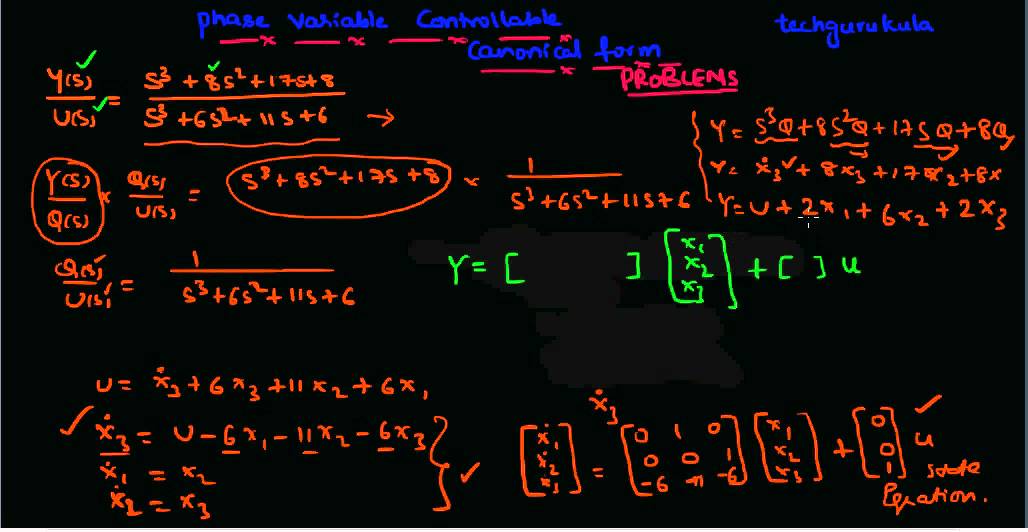
Controllable Canonical Form
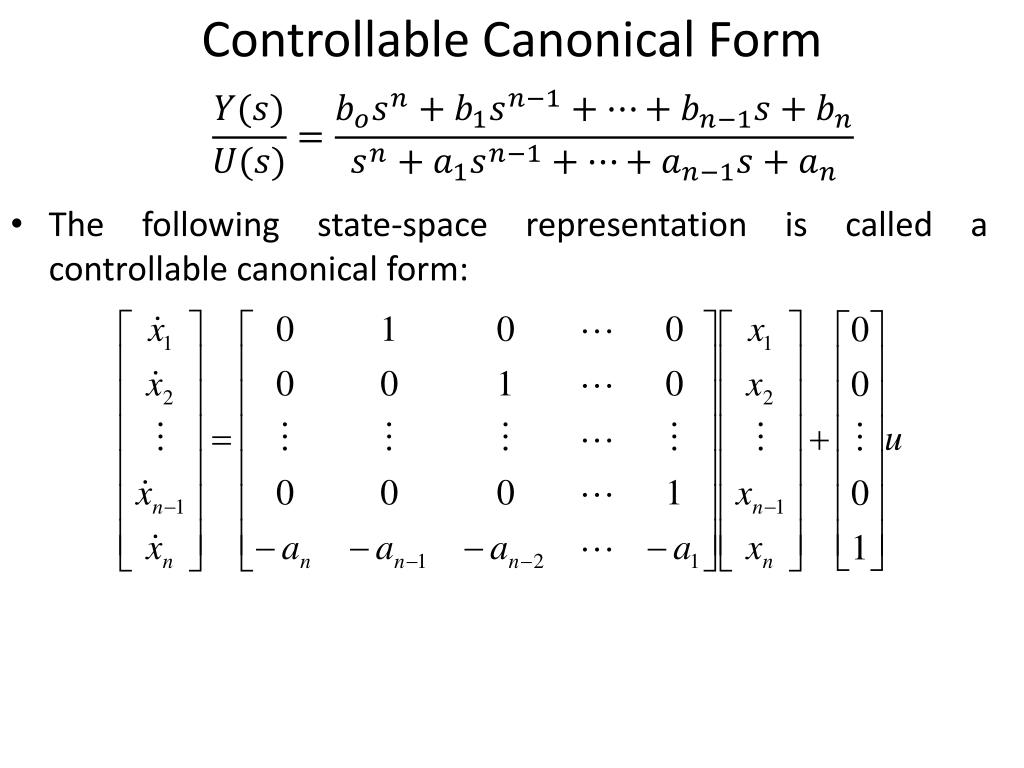
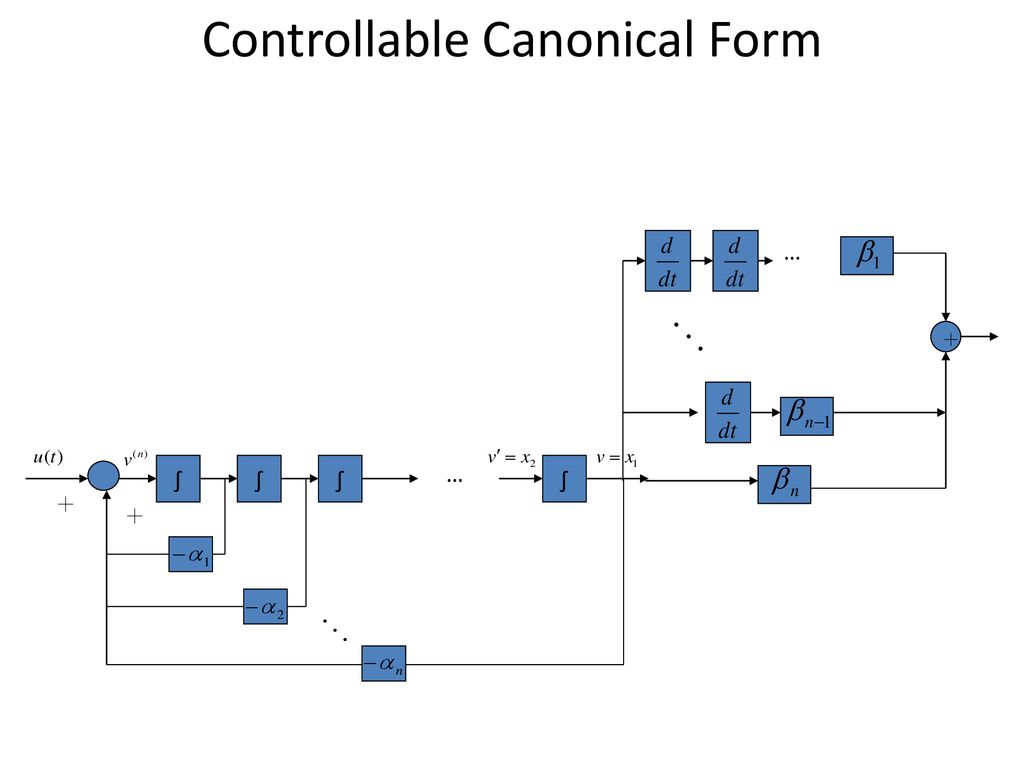
Controllable Canonical Form - This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the.
This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the.
This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function.
Feedback Control Systems (FCS) ppt download
We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k.
PPT Feedback Control Systems (FCS) PowerPoint Presentation, free
Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x..
Feedback Control Systems (FCS) ppt download
We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial.
State Space Introduction Controllable Canonical Form YouTube
Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond.
LCS 53a Controllable Canonical Form (CCF) statespace models YouTube
We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial.
Feedback Control Systems (FCS) ppt download
Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond.
Lecture 3 State Space Canonical forms YouTube
This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k.
Easy Explanation of Controllable Canonical Form Control Engineering
This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k.
Controllable Canonical Phase Variable Form Method 1 Converting
Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x..
controllable canonical form problem solving YouTube
Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. This realization is called the controllable canonical form uw linear systems (x. Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using..
This Realization Is Called The Controllable Canonical Form Uw Linear Systems (X.
Learn how to obtain controllable canonical form, a minimal realization of a system with the characteristic polynomial in the a matrix, using. Theorem (kalman canonical form (controllability)) let x 2rn, x(k + 1) = ax(k) + bu(k), y(k) = cx(k) + du(k) be uncontrollable with rank of the. We will see that there are multiple models (or realizations) that correspond to the same transfer function.
.jpg)


.jpg)