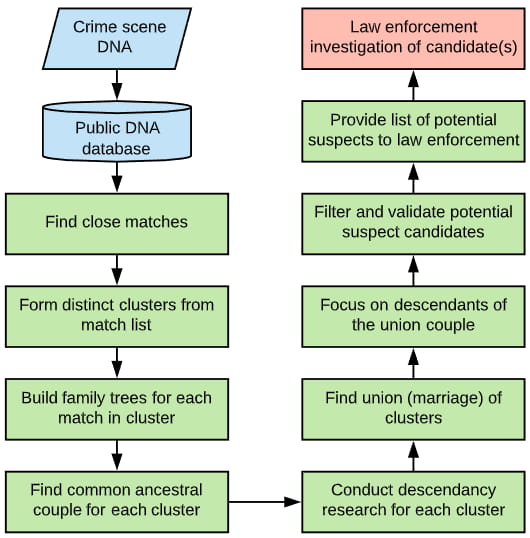
Forensic Investigative Genetic Genealogy
Forensic Investigative Genetic Genealogy - But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy). Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes.
Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy).
When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy). Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few.
The emerging field of Forensic Genealogy solving crimes using
But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg.
Investigative Genealogy How Does it Work?
But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify.
An Introduction to Forensic Genealogy Technology for Forensic
When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but.
An Introduction to Investigative Genealogy From Crime Scene
When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts.
Forensic Investigative Genealogy Resources for Law Enforcement
When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed.
Forensic Investigative Genealogy Resources for Law Enforcement
Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that.
The emerging field of Forensic Genealogy solving crimes using
Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy). Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to.
Investigative Genealogy How Does it Work?
But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy)..
Investigative Genealogy How Does it Work?
When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy). Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. But before any genetic genealogy takes place, a few. When a search does not result.
FI White Paper
When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy). When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy.
But Before Any Genetic Genealogy Takes Place, A Few.
Forensic genealogy is law enforcement’s use of dna analysis combined with traditional genealogy research to generate investigative leads for unsolved violent crimes. When a search does not result in a codis match, forensic science service providers (fssps) may identify leads using forensic genetic genealogy (fgg), a technique that combines traditional. Forensic dna analysis tries to do, forensic genetic genealogy attempts to use snp data to find relatives of the person that has committed a crime, or whose remains have been discovered but not identified. When a dna sample is extracted from a crime scene, it can identify a suspect through igg (sometimes referred to as forensic genealogy).