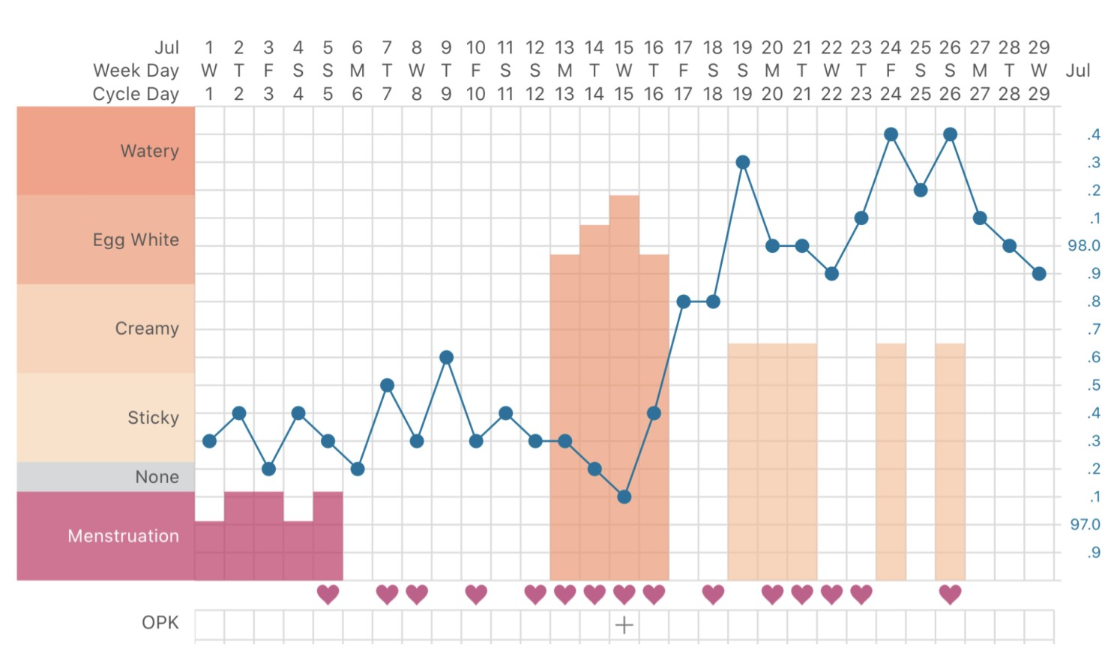
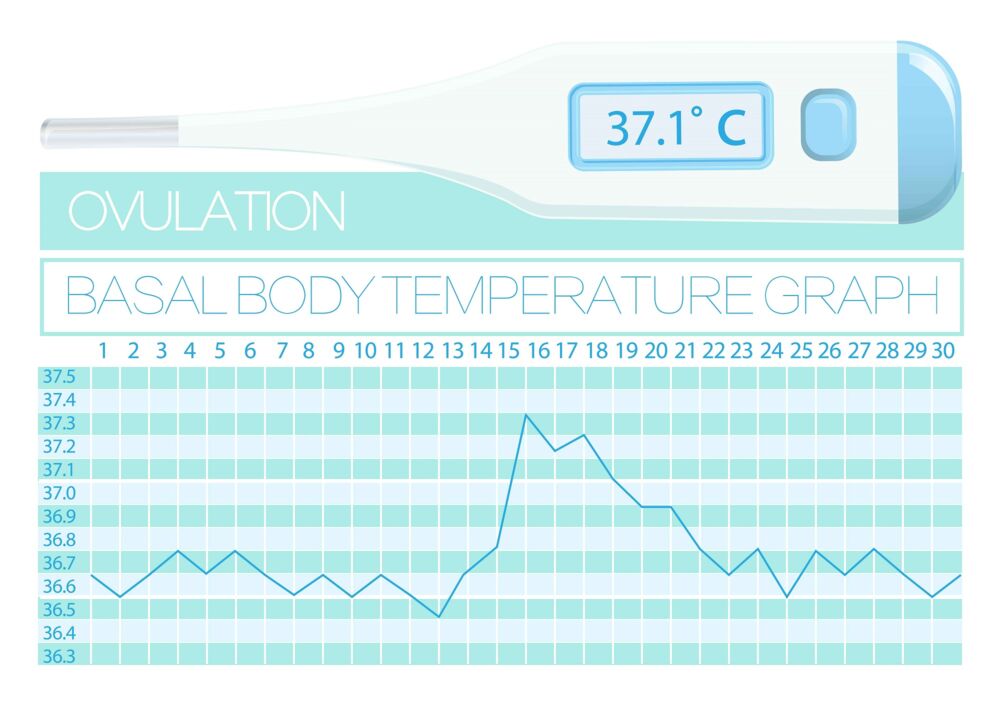
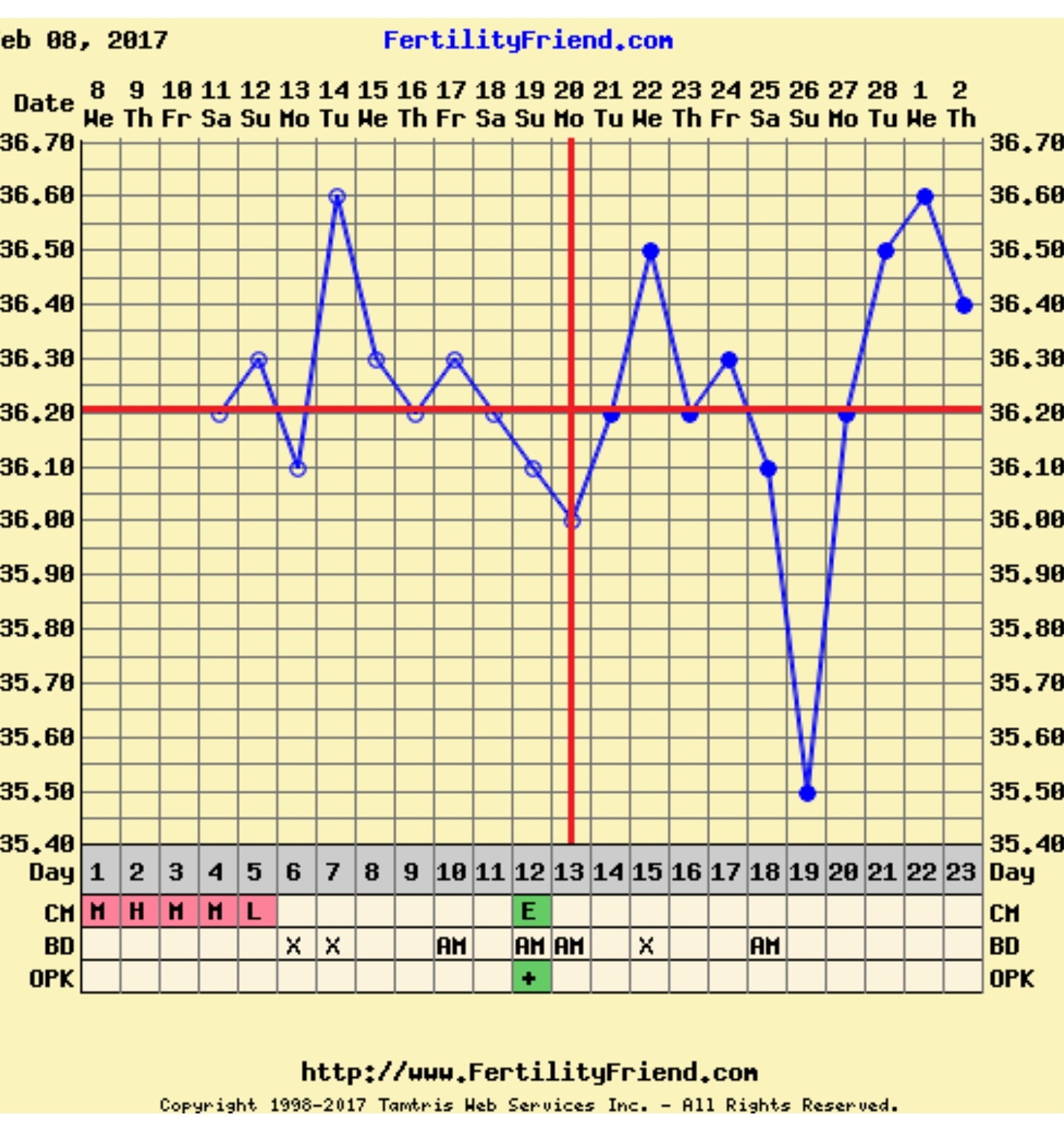
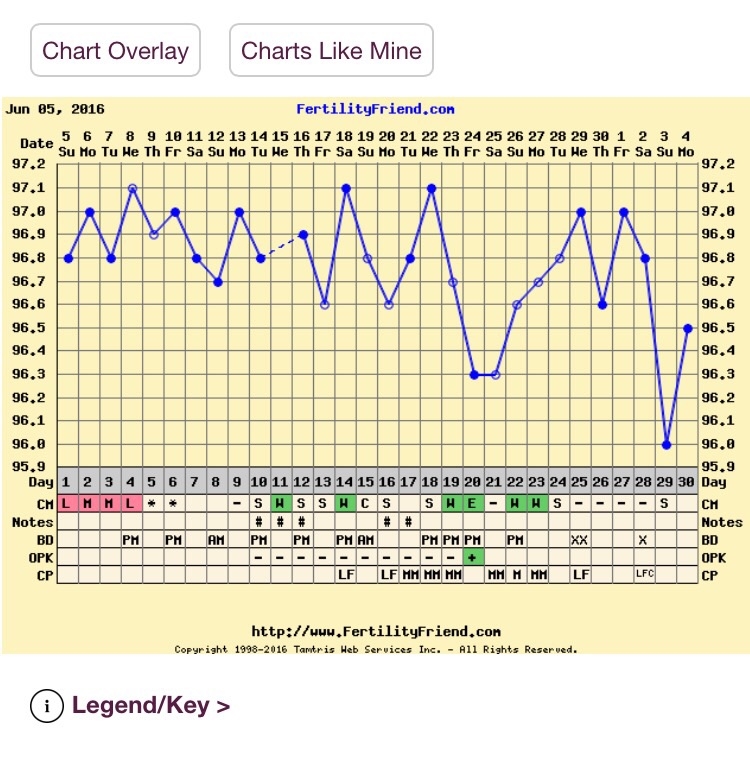
Low Bbt Temps After Ovulation
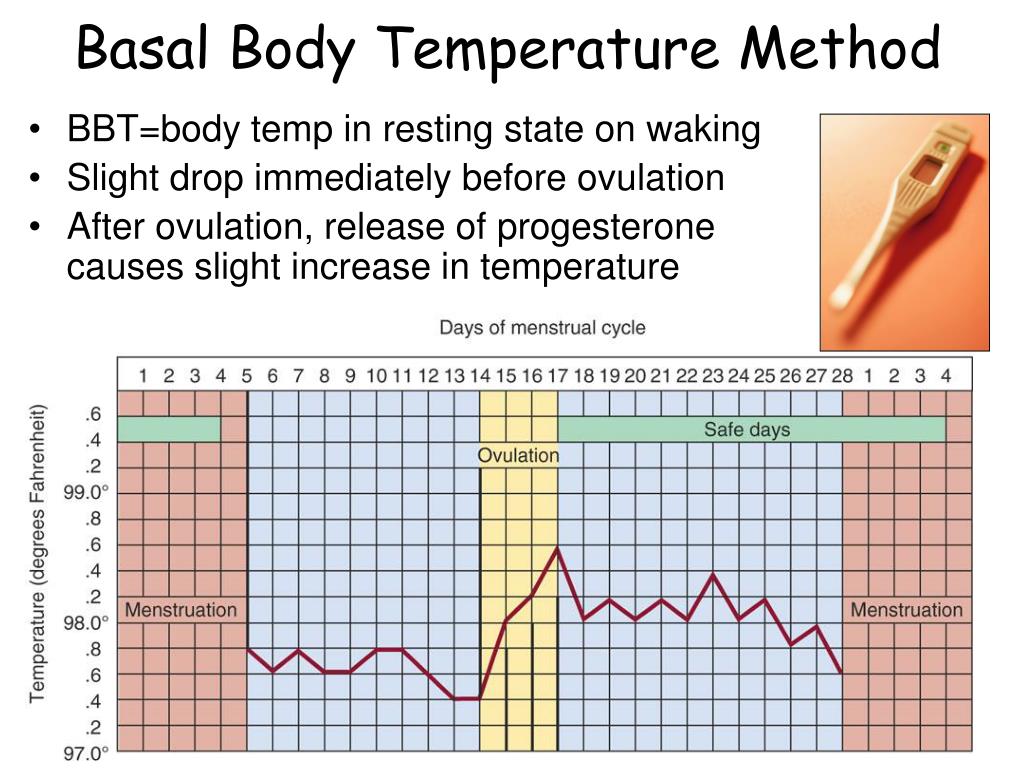
Low Bbt Temps After Ovulation - Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. What's a normal basal body temperature? The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation.
For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. What's a normal basal body temperature? Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels.
For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. What's a normal basal body temperature? This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0.
Kindara BBT Instructions — Rosenthal Women's Health & Fertility
The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. What's a normal basal body temperature? But the day after you ovulate, you.
Basal Body Temperature How to Measure BBT to Detect Ovulation
In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one.
Basal Body Temperature Chart BBT A woman's guide on how to read it
Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. What's a normal basal body temperature? Before ovulation, your bbt may range from.
BBT (Basal Body Temperature) Chart Everything You Need To Know Being
But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to.
Low BBT, low progesterone and ?gluten? — The Bump
But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of.
PPT Chapter 10 Contraception PowerPoint Presentation, free download
One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to.
Low bbt after ovulation?
One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. What's a normal basal body temperature? For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation. In the second case, a.
BBT chart help low temp after ovulation?
However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. The basal body temperature can drop before (a rise in estrogen) and after ovulation. What's a normal basal body temperature? In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo,.
BBT Chart Basal Body Temperature Chart BBT Chart For Ovulation
Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the.
BBT chart help low temp after ovulation?
In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. This rise in bbt is often referred to as the “temperature shift” and. Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact)..
This Rise In Bbt Is Often Referred To As The “Temperature Shift” And.
Before ovulation, your bbt may range from about 97 to 98 degrees f (97.2 to 97.7 degrees f, to be more exact). In the second case, a decrease in bbt occurs due to implantation of the embryo, with hormonal imbalance, or before the beginning of the period. What's a normal basal body temperature? For example, a drop in your basal body temperature after ovulation can have more than one explanation.
The Basal Body Temperature Can Drop Before (A Rise In Estrogen) And After Ovulation.
But the day after you ovulate, you should see an uptick of 0.5 to 1.0. Prior to ovulation, a woman’s bbt is relatively low and stable. However, after ovulation, bbt tends to rise due to an increase in progesterone levels. One day before ovulation, a luteinizing hormone peak is observed, which can be accompanied by an additional decrease in.