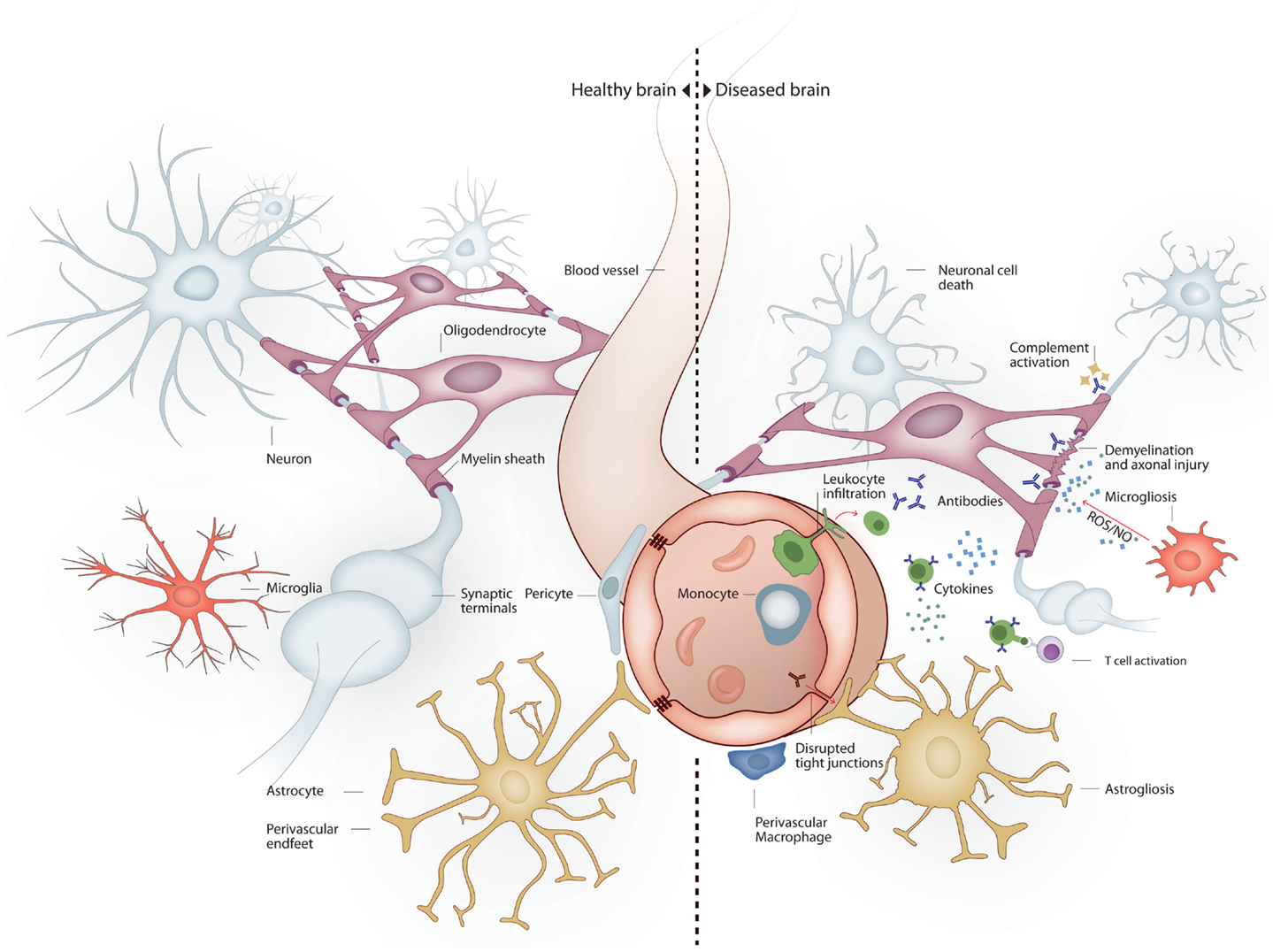
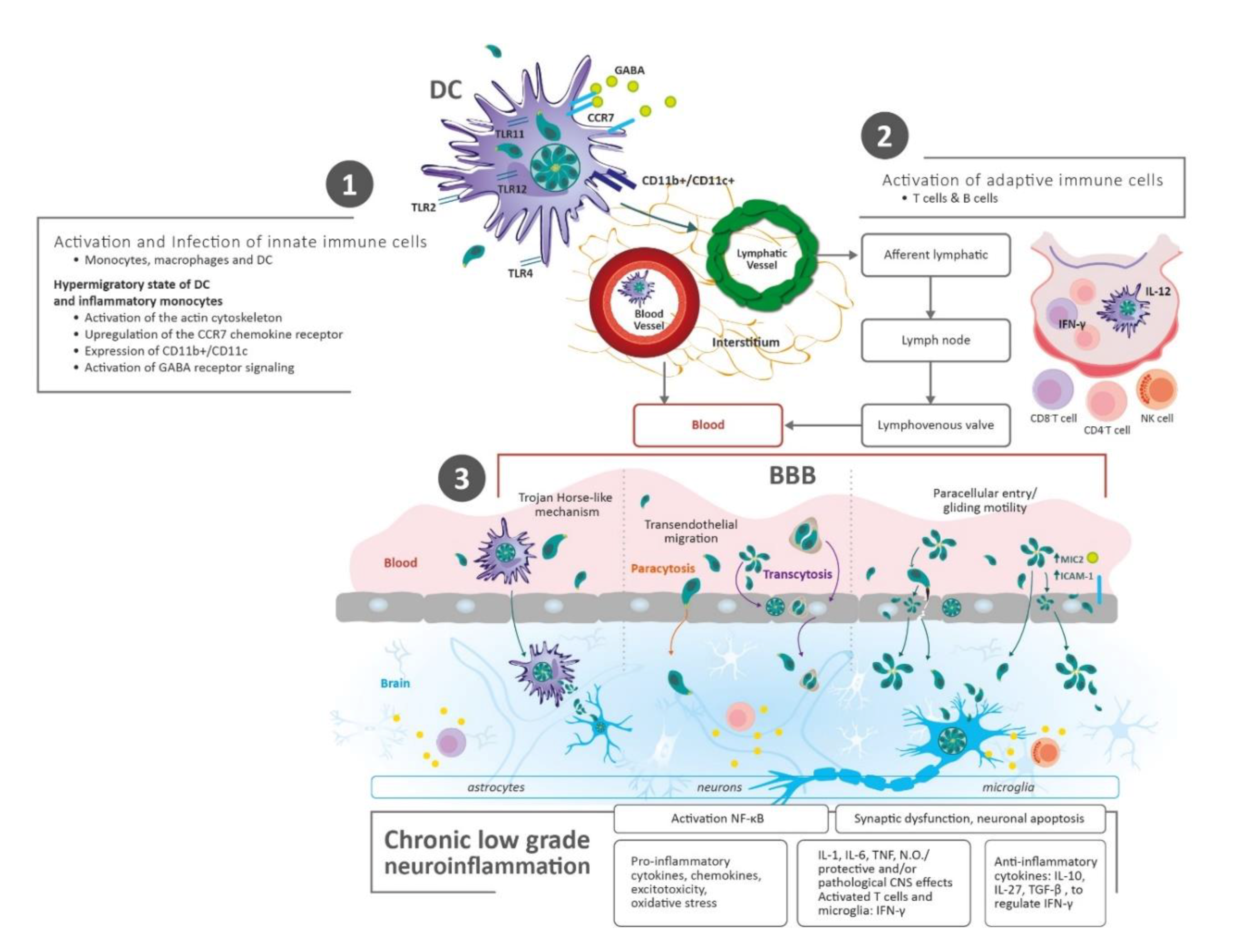
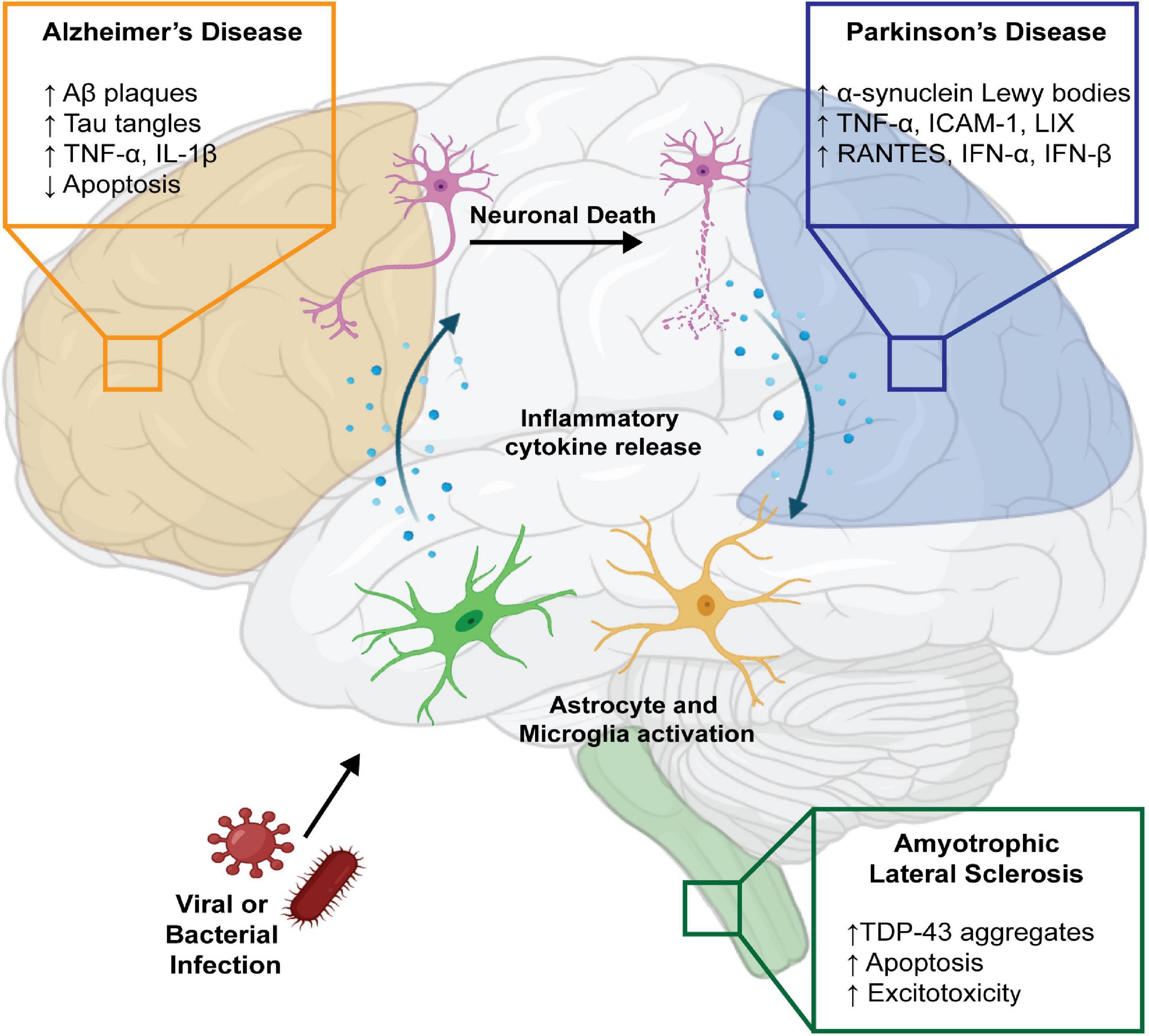
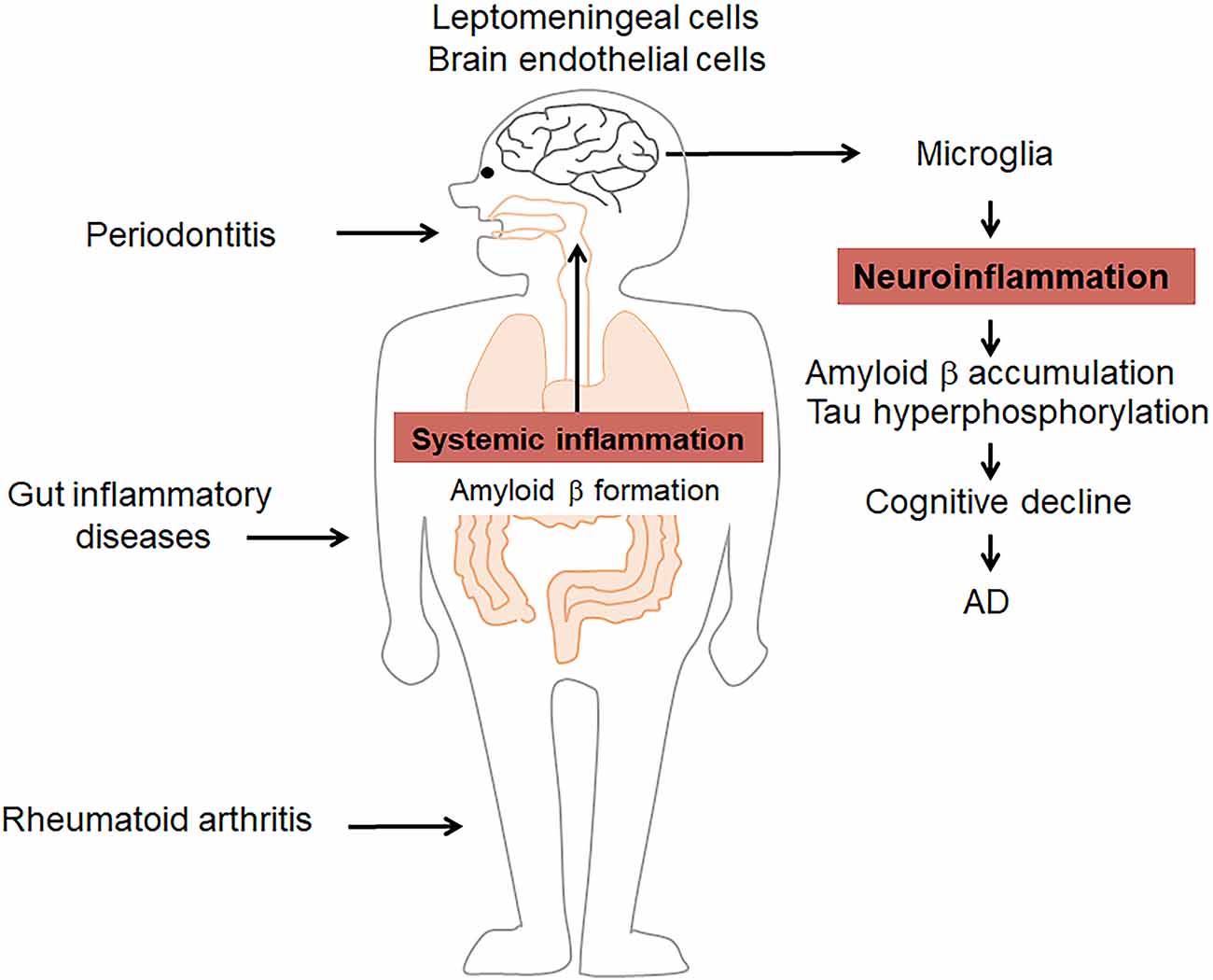
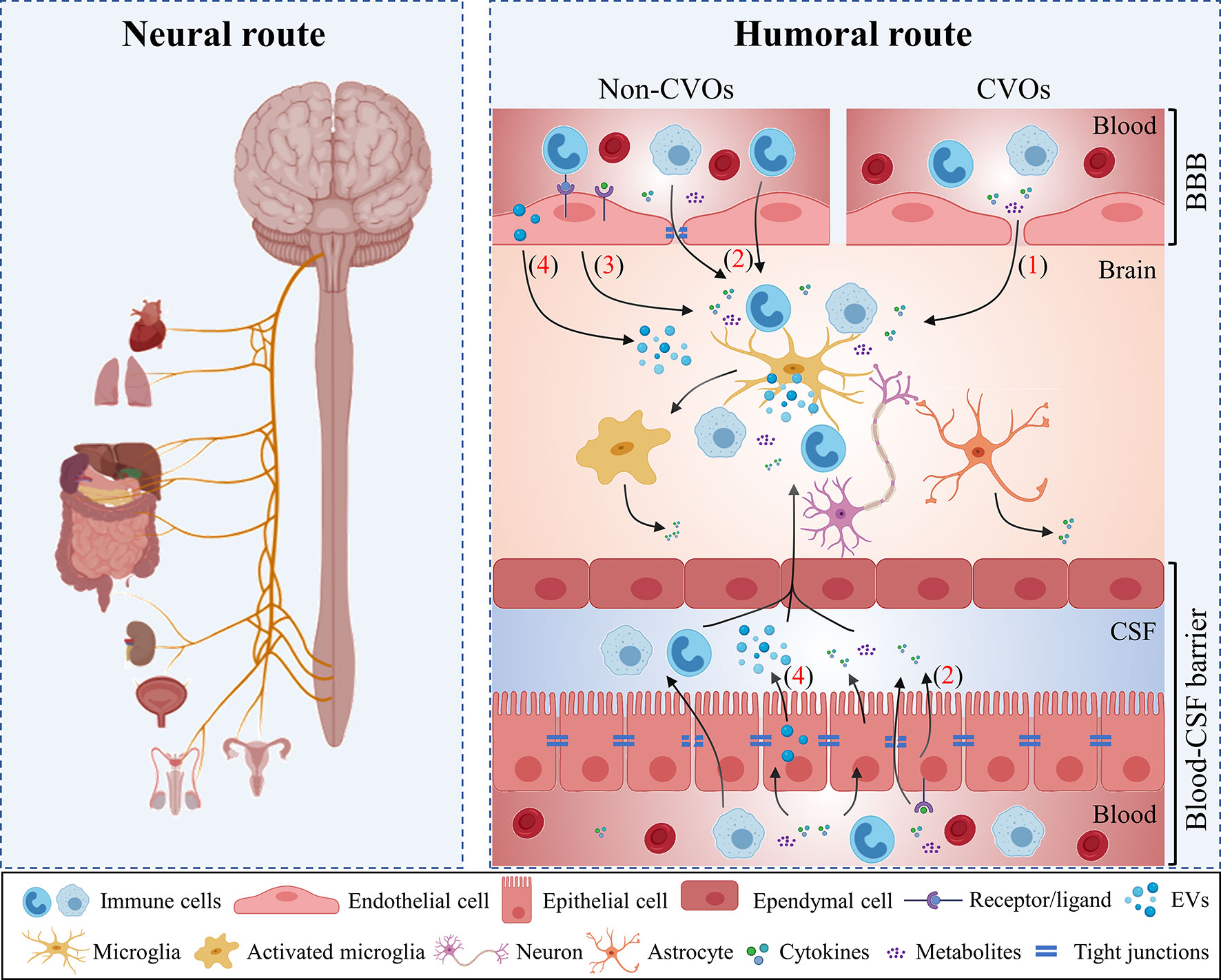
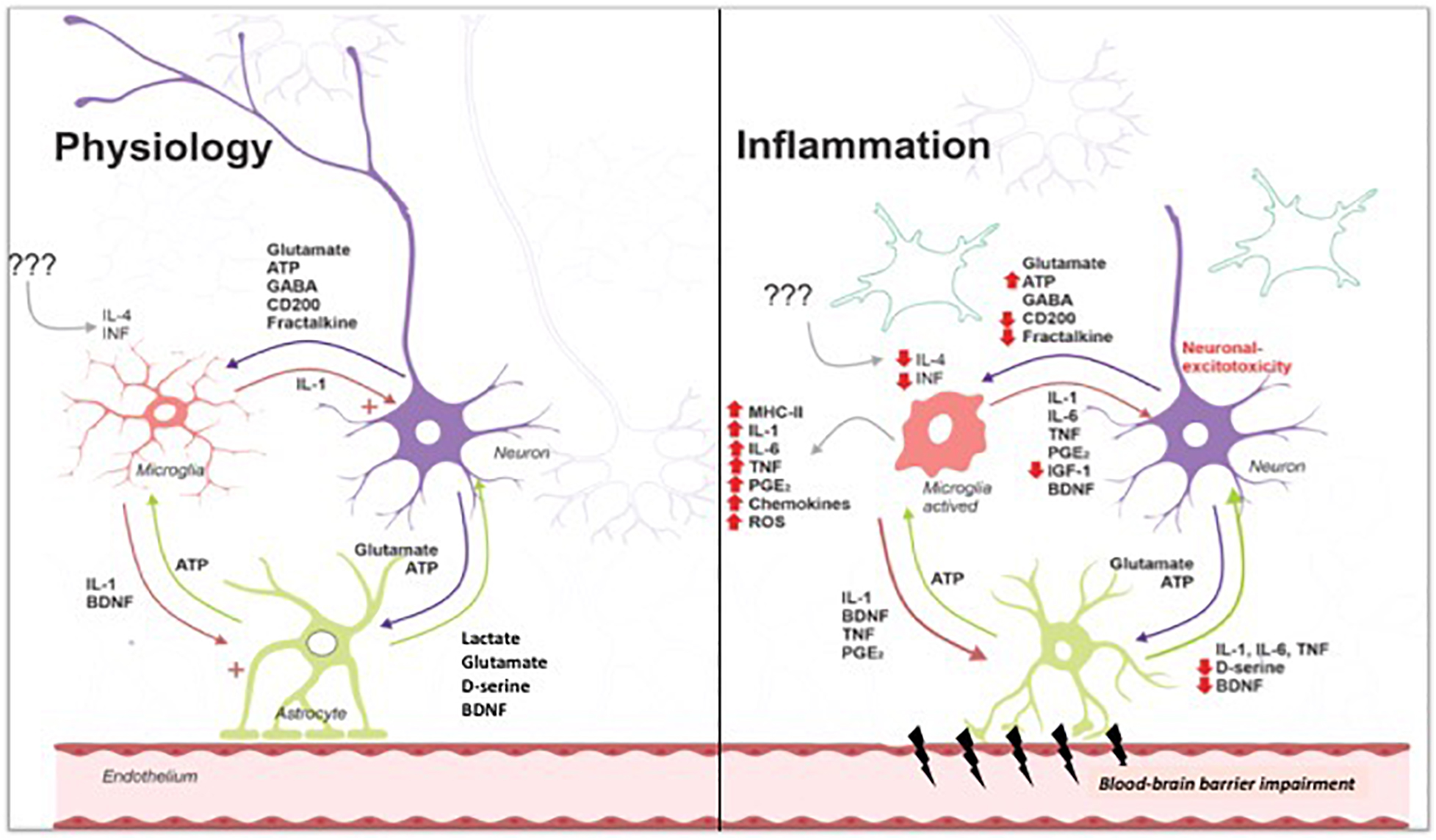
Systemic Infections May Cause Cognitive Deterioration And Neurodegeneration
Systemic Infections May Cause Cognitive Deterioration And Neurodegeneration - Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease.
Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease.
Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;.
Frontiers Systemic Inflammation and the Brain Novel Roles of
Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. 1 department of neurology, national.
Brain Sciences Free FullText Pathophysiological Mechanisms of
Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger.
Frontiers Microbial Infections Are a Risk Factor for
Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Given that severe.
Frontiers Systemic inflammation, bloodbrain barrier vulnerability
Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a.
Neurological involvement of COVID19 from neuroinvasion and
Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Central nervous system (cns).
Inflammation and cognitive impairment in OSAS. CIH, the characteristic
Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Common infections, including.
Frontiers Inflammation Spreading Negative Spiral Linking Systemic
1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation,.
Microbes on the Mind A Complex Role in Neurodegeneration
Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Common infections, including.
Frontiers The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Alzheimer’s Disease
1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Common infections, including.
Frontiers Systemic Response to Infection Induces LongTerm Cognitive
Common infections, including flu and herpes, may increase dementia risk by contributing to brain volume loss, particularly in. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a.
Common Infections, Including Flu And Herpes, May Increase Dementia Risk By Contributing To Brain Volume Loss, Particularly In.
Central nervous system (cns) infections have been suggested to act as a possible trigger for neurodegenerative diseases such as. Given that severe acute infections and various chronic infectious diseases trigger systemic and neurologic inflammation, both have been. 1 department of neurology, national taiwan university hospital;. Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease.