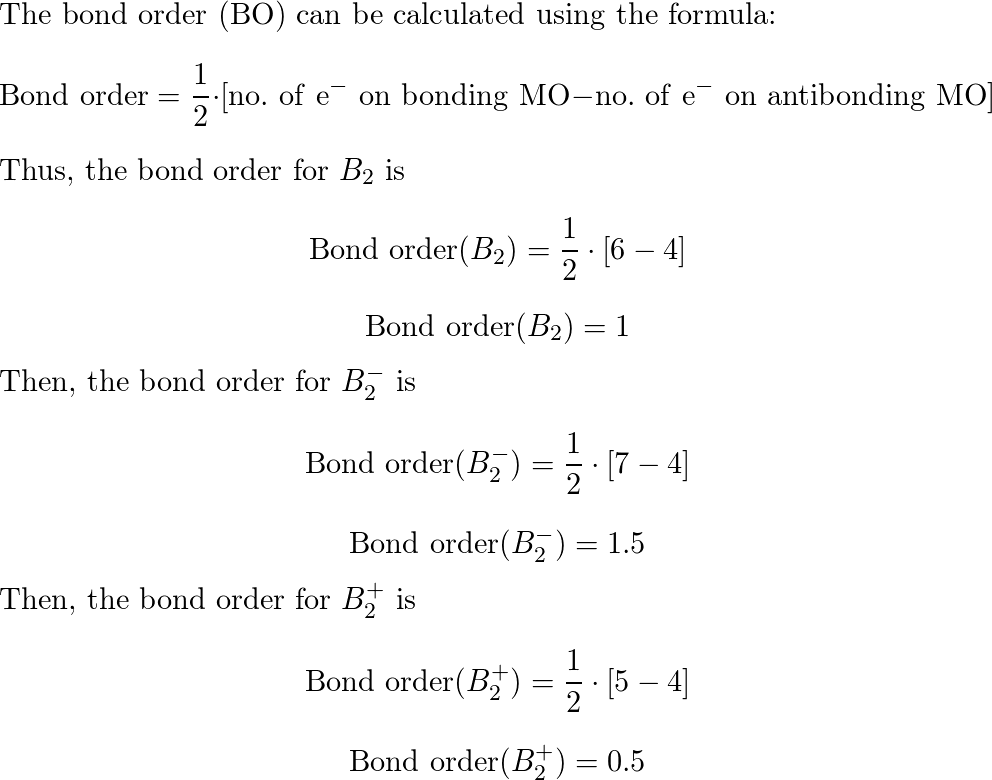What Is The Bond Order Of B2
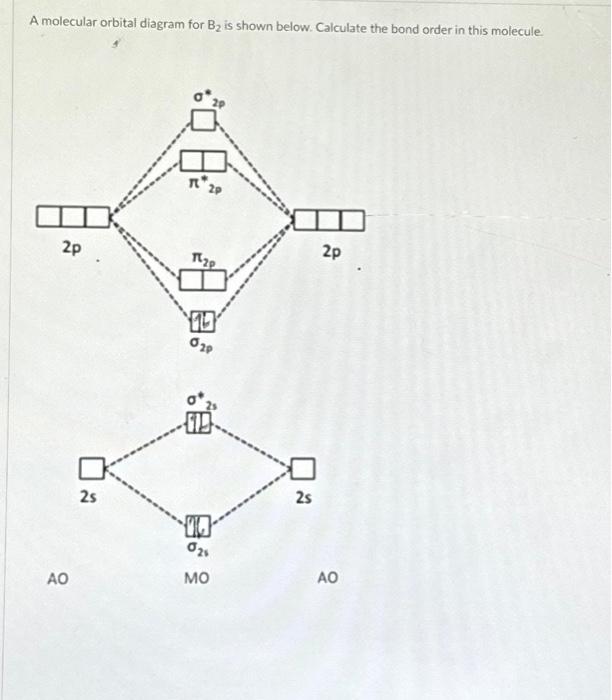
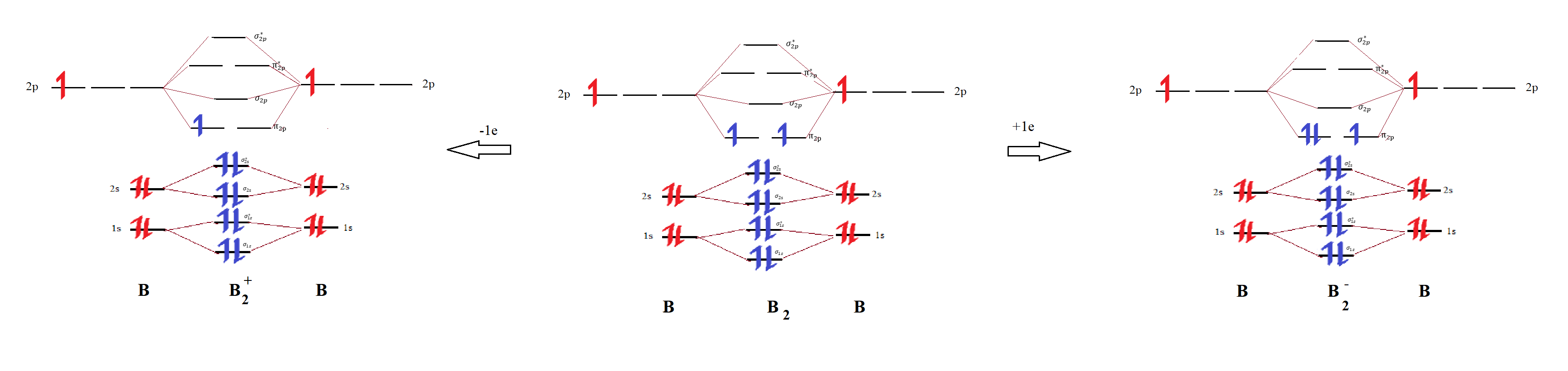
What Is The Bond Order Of B2 - The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. The bond order of b 2 molecule: This means that the electrons are effectively shared.
This means that the electrons are effectively shared. The bond order of b 2 molecule: Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule.
This means that the electrons are effectively shared. The bond order of b 2 molecule: The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding.
BOND ORDER of B2 Molecule Bond order of BORON MOLECULE YouTube
The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference.
Solved A molecular orbital diagram for B2 is shown below.
Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of.
Solved 31) Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to
The bond order of b 2 molecule: Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. This means that the electrons are effectively shared. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the.
F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Bond Order
The bond order of b 2 molecule: A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by.
붕소 루이스 점자점식 지식iN
Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. By analyzing.
define bond order and calculate the bond order in B2 Chemistry
This means that the electrons are effectively shared. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between.
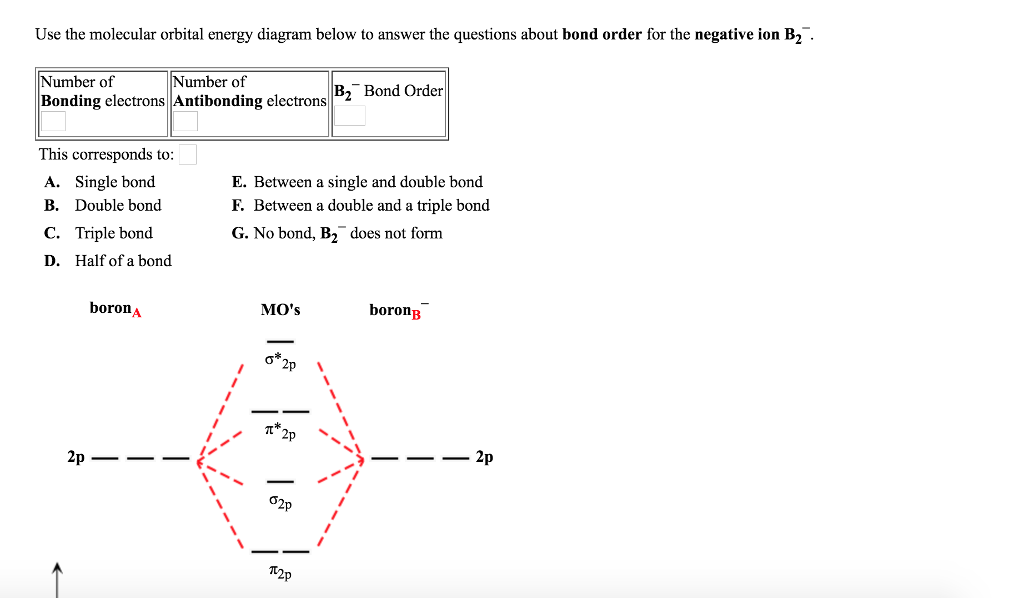
Solved Use the molecular orbital energy diagram below to
By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with.
16. Explain Bond order of B2.
By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. This means that the electrons are effectively shared. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. The bond order of b 2 molecule: The b.
Use MO diagrams to place B2+, B2, and B2 in order of decr Quizlet
The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. The bond order of b 2 molecule: By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding. Bonding orbitals are marked with.
Molecular Orbital Diagram For B2
Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. A bond order of 2 indicates a stable and strong bond between the boron atoms in the b2 molecule. The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. The bond.
The Bond Order Of B 2 Molecule:
The b 2 molecule is known to be formed by the combination of two boron atoms, where they are linked by a covalent bond. This means that the electrons are effectively shared. Bonding orbitals are marked with sigma or pi and antibonding orbitals with sigma* or pi*. By analyzing the mo diagram for b2, we can determine the bond order, which is the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding.